The Indian Audit and Accounts Department
Indian Audit and Accounts Department has a unitary structure in a federal setup. The Indian Audit and Accounts Service (IAAS), a formalized civil services cadre of the Union of India, forms the middle and top level management of the organization, through which the Comptroller and Auditor General of India exercises its mandate. The 600 odd IAAS officers have a multi-disciplinary academic background and include experts in various fields.
The IAAS officers, while working for a constitutional authority, have the benefits of a working environment which promotes pursuit for professional excellence in public service without fear or favor.
Working in these offices an IAAS officer has the opportunities to work in areas which interface with diverse arms and tiers of the Government. Be it armed forces, large public service under takings or village panchayat, an IAAS officer has the opportunity to experience and contribute to the public good in all facets of government.
The officers are drawn from diverse academic and professional disciplines such as financial management, accountancy, costing, law, engineering, and economics and so on. Quite a few of them have excellent exposure to information technology. The officers attend specially designed executive development and management development programmes at suitable intervals. They are deputed to a variety of studies and training relevant to the work in the department organized by other institutions within and outside the country. They are also placed on secondment to Union/State Governments. The experience thus gained is of great help in the discharge of audit functions. Conferences and Workshops participated in by senior officers are held periodically to discuss the problems faced in the department and to find solutions to them.
The officers directly recruited to the service are exposed to a foundational course at the National Academy of Administration, and imparted professional training - theoretical and practical - at the National Academy of Audit and Accounts and the National Institute of Financial Management in the areas of accounting and auditing, financial management, personnel regulations, cost and management accounting, management concepts, quantitative techniques and electronic data processing. This is supplemented by practical training in the field formations of the department. During this period, the officers are also required to qualify in two professional examinations conducted by the Department. The officers promoted to the service also go through on intensive orientation course. The IAAS Officers are valued in the bureaucracy for their multi-faceted experience and expertise in the area of Audit, Accounts and finance. Not surprisingly, several of them have stints in key positions in the union ministries of Government of India. The IAAS Officers work in an environment which promotes continuous professional up-gradation. With increasing international exposure due to collaborative working framework of Supreme Audit Institutions of the world, auditing international bodies like the UN, WHO, and bilateral/multilateral assignments with other countries, the IAAS officers stay on the cutting edge of the profession. Valued world over they are sought after internationally. IAAS Officers have been borrowed out to organizations like the United Nations, IDI and various other countries for their expertise and skills.
|
Organization of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department |
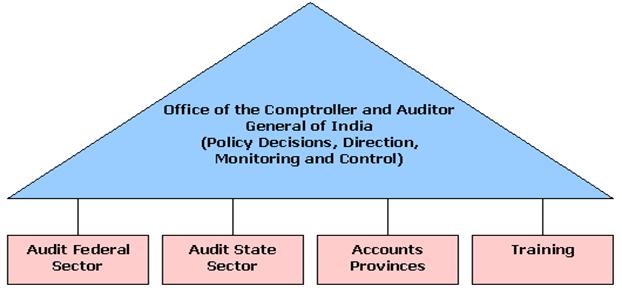
The Comptroller and Auditor General of India discharge his multifarious duties through the Indian Audit and Accounts Department. The Department consists of about fifty thousand employees and is functionally organised into 104 specialised formations throughout the country
At the apex of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department is the office of the Comptroller and Auditor General which directs monitors and controls all activities connected with audit, accounts and entitlement functions of the Department. It is responsible for development of organisational objectives and policies, audit standards and systems, management of the manpower and material resources of the Department and final processing and approval of the Audit Reports. For carrying out these responsibilities, it has been organised on a functional basis and there are separate divisions dealing with Accounts and Entitlements, Civil Audit, Railway Audit, Commercial Audit, Revenue Audit, Administration of Cadres, Training, Organisation and Methods, Inspection of field offices, EDP etc. These divisions are headed by the Deputy / Additional Deputy Comptroller and Auditor General and Principal Directors.
Offices of the Accountants General (Audit) are responsible for audit of all receipts and expenditure of the Provincial Governments, and audit of Provincial Government companies, corporations and autonomous bodies.
Offices of the Principal Directors of Audit are responsible for audit of the activities of the Federal Government, including Civil Ministries and Departments, Overseas Establishments, Defence, Indian Railways and Posts and Telecommunications.
There is a separate organisational set up for the audit of Federal Public undertakings. At the apex of this organisation is the Deputy Comptroller and Auditor General (Commercial). The organisation is responsible for:-
Test Audit/Supplementary Audit of transactions of Government Companies/ corporations, which finds final expression in an annual Audit Report bringing out selected topics of interest relating to them.